One of the most common questions in this period of our lives is whether it is more convenient to use a die-cutting machine or a digital cutting machine. Large companies offer both die-cutting and digital cutting to help their customers create unique shapes, but what the difference is between them is not clear to everyone.
For most small companies without such solutions, it's not even clear which solution they should purchase first. As experts, we often find ourselves in the uncomfortable position of having to answer this question and provide advice. Let's first try to clarify the meaning of the terms "die-cutting" and "digital cutting".
What is die-cutting?
In printing, die-cutting provides a quick and inexpensive way to cut large quantities of print into the same shape. Artwork is printed on square or rectangular material (usually paper or card stock) and then placed in a machine with a custom "die" or "punch block" (a wooden block with a metal blade) that is bent and folded into the desired shape). As the machine presses the sheet and dies together, it cuts the shape of the blade into the material.
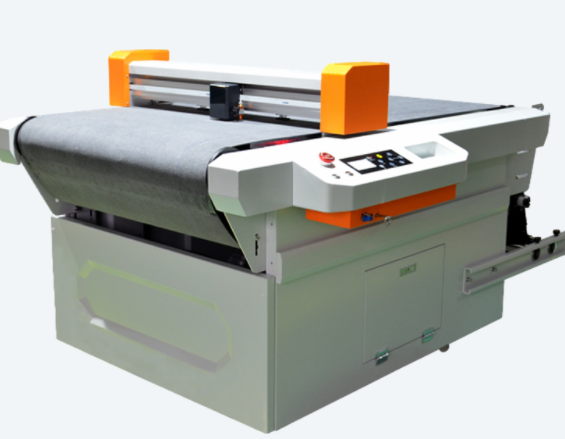
Flatbed Digital Cutter
What is digital cutting?
Unlike die cutting, which uses a physical die to create a shape, digital cutting uses a blade that follows a computer-programmed path to creating the shape. A digital cutter consists of a flat table area and a set of cutting, milling, and scoring attachments mounted on an arm. The arm allows the cutter to move to the left, right, forward and backward. A printed sheet is placed on the table and the cutter follows a programmed path through the sheet to cut out the shape.
Which is the better option?
How do you choose between two cutting solutions? The simplest answer is, "It all depends on the type of job. If you want to cut a large number of small items printed on paper or card stock, die cutting is the more cost-effective and time-saving option. Once the die is assembled, it can be used over and over again to create a large number of the same shapes - all in a fraction of the time of a digital cutting machine. This means that the cost of assembling a custom die can be offset by using it on a large number of items (and/or reusing it in the future for additional print runs).
However, if you are looking to cut a small number of large format items (especially items printed on thicker, tougher materials), a digital cutter is a better choice. There's no need to pay for custom tooling; plus, you can create more complex shapes with digital cutting.
Flatbed Digital Cutter
According to market research and industry journals, the printing market is experiencing a period of high growth in the digital sector. This is mainly due to a sharp decrease in the number of orders, but a significant increase in the variety of demand.
Typesetting is increasingly faced with the demand for small quantities, custom jobs, fast delivery, and competitive prices, which are not suitable for offset printing and die-cutting processes.
From this assumption, we come to the question, what should be done to meet this demand? My personal interpretation is to equip yourself with a "smart" product that can meet quality, versatility, and fair productivity.
Print Media
Every manufacturer claims to have the highest quality products, so the next question is, what are the parameters that guide our judgment? Reputation in the marketplace is certainly an important factor, as is value for money, but I suggest considering other aspects: the actual cost of use, available support, additional services, warranty terms, ease of use, and installation and training time.
Versatility is another important aspect that determines the range of work that can be performed, the types of materials that can be processed, and the longevity of the investment. This last aspect is important because, given the hypothetical lease, the machine must meet its needs for a period of at least as long as the lease.
Finally, your new equipment should have a fair production capacity that can meet the actual demand - not just expectations.